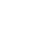The process of defining custom objects starts with creating a custom object, defining its general properties, and saving the object. Note that this process may be a complex and lengthy procedure.
Note: Before users can view custom objects, you must assign the corresponding object rights to their group. Each Custom Object has its own set of rights.
There are two approaches to creating a custom object: Copy an existing object definition, or create an object definition from scratch.
If the object to be created will have a definition similar to an existing object definition, you can copy the definition of the existing object, then modify the copy to reflect the exact properties you want in the new object definition. This may save time compared to creating the entire new object definition from scratch.
Continue defining object properties
Regardless of which approach you used to create the custom object, you should now continue defining its properties as explained in Customization Sequence.
Once the object properties match your solution design, the object is defined and displayed on the Object Definition List screen. For details, see Viewing Object Definitions.
Resulting User Interface and Other Changes
When you save the custom object information, the following events take place:
•You see the Create Involved and Create Milestone buttons at the top of the General tab.
Create Involved and Create Milestone Buttons
•Two document folders with the object's name are automatically created in the Documents area and added to the following directories:
oTop Level/System/Object Definitions/Object Name
This folder stores all documents related to the design of the object definition, such as XML files for custom blocks, Involved and Milestone object definition files, document templates, and rules.
oTop Level/Attachments/Object Name
This folder stores all of the files that are uploaded to the object records.
Important: For each object record, this folder is created only when the record is saved and end users access the Documents block of that record for the first time.
For more details on document folders, see the Administration Guide.
For a complete overall procedure of defining custom objects, see Creating Custom Objects.